The attached User Guide shows how ’ ’ and a null value is handle in composite datasource.
Different datasources have different interpretations for EMPTY (’ ') and NULL value.
What is the differences between ’ ’ and NULL value?
-
An ’ ’ value is a “field-formatted” value with no significant data in it.
-
A NULL value represents the absence of a value for a record in a field.
-
Null has no bounds; it can be used for string, integer, date, etc. fields in a database. An empty string is just regarding a string; it’s a string like ‘abcdef’ but without length.
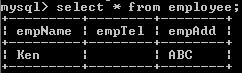
Example on ’ ’ value:
SQL Statement:
CREATE TABLE Employee(empName VARCHAR(20), empTel VARCHAR(20), empAdd VARCHAR(20));
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES('Ken','','ABC');
Output:
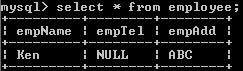
Example on NULL value:
SQL Statement:
CREATE TABLE Employee(empName VARCHAR(20), empTel VARCHAR(20), empAdd VARCHAR(20));
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES('Ken',null,'ABC');
Output:
Note: It is recommended to use a Null value to indicate no data is available.
HowEmptyValueIsHandleInCMP.pdf (304.1 KB)